
Nov 19 2018.
views 1684Glycemic index (GI), refers to how fast glucose is released to the bloodstream after digesting the ingested food. 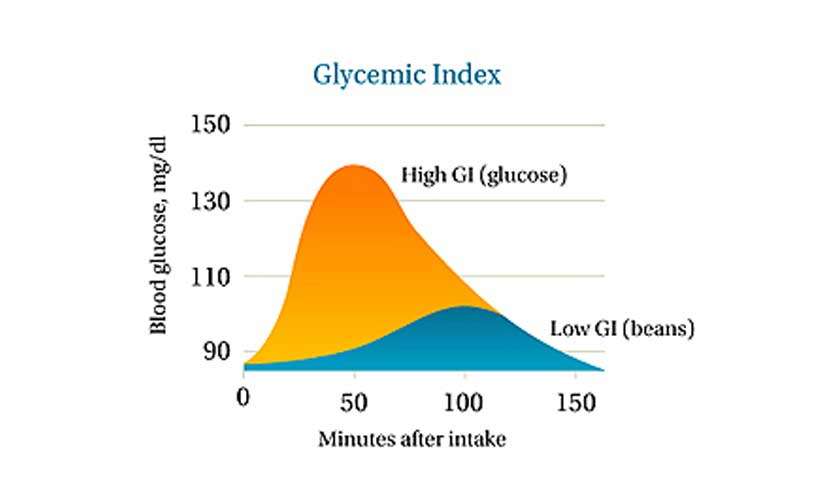 Generally, any digested food gets digested and released to the bloodstream within the course of two hours. It is quite important that the blood sugar levels are maintained without heavy spikes. In a healthy adult, before meals, the blood sugar levels should be less than 100mg/dl and after meals it can go up to 120mg/dl. Huge spikes exceeding the upper limit, can cause blindness, kidney failure and impose a cardiovascular risk. In addition, such increments happening regularly can lead to cell receptors in the pancreas and in the body to be unresponsive to sugar levels which will give rise to type II diabetes.
Generally, any digested food gets digested and released to the bloodstream within the course of two hours. It is quite important that the blood sugar levels are maintained without heavy spikes. In a healthy adult, before meals, the blood sugar levels should be less than 100mg/dl and after meals it can go up to 120mg/dl. Huge spikes exceeding the upper limit, can cause blindness, kidney failure and impose a cardiovascular risk. In addition, such increments happening regularly can lead to cell receptors in the pancreas and in the body to be unresponsive to sugar levels which will give rise to type II diabetes.
Because of these immense threats, high sugar levels impose a parameter called glycemic index was developed. This is created on the base that glucose or sugar has a GI of 100, with the assumption that any ingested sugar gets readily released to the bloodstream. All the other food and beverages are given a GI value compared to sugar which has a GI of 100. Following are some of the foods and their GI values.
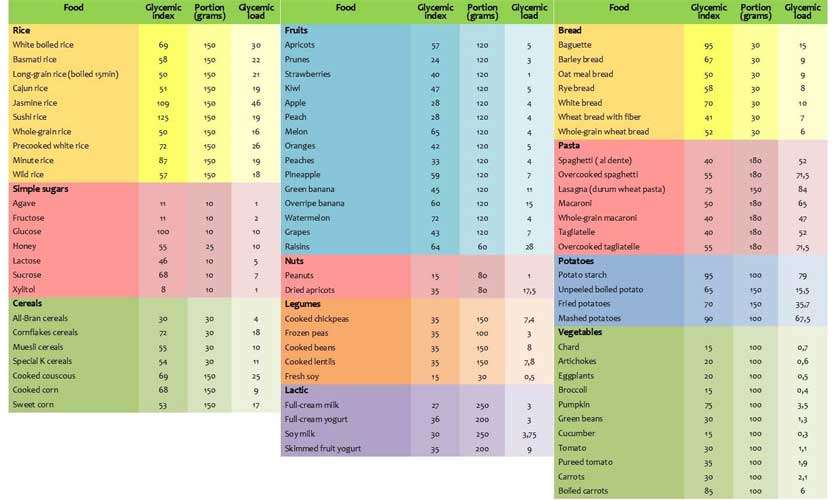
Low GI (55 or less)
Whole wheat bread
Oatmeal (rolled or steel cut), oat bran, muesli
Pasta, barley
Sweet potato, corn, yam, peas, legumes and lentils

Medium GI (56 – 69)
Whole wheat, rye and pita bread
Quick oats
Brown, wild or basmati rice, couscous

High GI (70 or more)
White bread or bagel
Cornflakes, bran flakes, instant oatmeal
Short grain white rice, rice pasta, macaroni and cheese from mix
Pumpkin
Pretzels, popcorn, crackers
Melons and Pineapple

A low GI indicates that the glucose is released to the bloodstream slowly, whereas a high GI shows that sugar is released much faster to the bloodstream. Food of high GI is of importance to athletes and people who engage in work that requires a much higher level of energy than the regular amount and such food will give the needed glucose levels to produce high amounts of energy. As humans mainly depend on aerobic respiration, providing enough of glucose to keep the body healthy is very important. For a person who is on a meal plan trying to lose weight, accompanying the diet plan with low GI food can give better results. Low GI food, give out sugar slowly because it takes time to digest such food, so it remains in the gut for a considerable amount of time leaving the person full for a while, which is very important to lose weight. This is a very important parameter for diabetic patients, so that their blood sugar levels can be properly maintained omitting the foods that give instant sugar highs.
Reasons for Higher or Lower GIs in Food
Fat and fiber generally decrease the GI of a food and also if a food is highly cooked or processed, its GItend to be much higher. In addition, ripened fruits have higher GI levels whereas ripe vegetables have lower GI values. Because with ripening pf fruits, the amount of simple sugars increases and most of the complex carbohydrates (which includes fibers) and other complex polymers are degraded, making digestion easier and when a vegetable ripens, the reverse happens, making it harder to digest. Different processing steps such as juicing of fruits (as opposed to the whole fruit), mashing potatoes (as opposed to whole baked potato) increases the GI values.
GI Alone is Not Enough
GI doesn’t give an indication of the total sugar levels or the total calorie levels of the foods. Pork tends to have a lower GI because its fat content is high and sugar level is low, which is the case with many types of meat, but pork has a very high-calorie level owing to its high-fat quantity. High levels of pork consumption is linked with many health implications and chicken is a much healthier choice to have in the diet, than pork. In addition, even though watermelon has a very high GI, its total calorie levels are very low because it's mostly water in the fruit, so it’s not really unhealthy to eat. So it’s important to consider the total calorie level, sugar level and fat level among other parameters along with GI to get a clear understanding of a food and its impact on health and overall functionality of the body.
0 Comments